1914 photograph of the bust of Queen Sobekneferu that was lost in WWII (Photo: Wikimedia Commons, Public domain)
The title of pharaoh is synonymous with the grandeur of the ancient Egyptian civilization. This name—which means “great house” in hieroglyphics—was given to the rulers who led this large empire. And while the majority of these figures were men like King Tut and Ramesses II, there were a few influential women who earned the title. The first recorded female pharaoh was Sobekneferu.
After the death of Amenemhat IV, who may or may not have been her brother and husband, Sobekneferu assumed the throne. Although her reign only lasted about four years, she was the first known female ruler to adopt the full royal titulary and to be recorded in the Turin King List—a recording of ancient Egyptian kings written on papyrus. Her end as ruler marks the end of the Twelfth Dynasty of the Middle Kingdom of Egypt.
Here we will learn more about Sobekneferu and her significance.
Who was Sobekneferu?

Right: Bust of Amenemhat III, father of Sobekneferu (Photo: ArchaiOptix via Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Left: 1914 photograph of the bust of Queen Sobekneferu that was lost in WWII (Photo: Wikimedia Commons, Public domain)
Sobekneferu was the first recorded female pharaoh to rule ancient Egypt and the last ruler of the Twelfth Dynasty of the Middle Kingdom (c. 2055 BCE – 1650 BCE). She was one of the daughters of the pharaoh Amenemhat III, although it is unknown which of his wives was her mother.
Her ascension to the throne is also unclear, but it is postulated that after Amenemhat IV died—the heir of Sobekneferu's father who may or may not have been her brother—she was put forth as the next pharaoh in absence of another male heir. Her relationship to Amenenhat III helped her assert legitimacy as a ruler.

Right: Bust of Sobekneferu in the Louvre (Photo: Neithsabes via Wikimedia Commons, Public domain)
Left: Photo of the Karnak List of Kings in the Louvre (Photo: Mbzt Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA 3.0)
Reign as Pharaoh
When she became pharaoh, Sobekneferu adopted the full royal titulary, which was the customary naming convention consisting of five names used by pharaohs. She based her first name on the crocodile-headed god Sobek associated with pharaonic power, fertility, and military prowess.

Jean-François Champollion, Illustration of Egyptian god Sobek, 1823–1825 (Photo: Brooklyn Museum via Wikimedia Commons, Public domain)
According to the Turin King List, Sobekneferu ruled for a total of 3 years, 10 months, and 24 days. Not much is known about her time as ruler, but it is believed that the Northern Mazghuna pyramid—an incompleted structure—may have been intended for her.
Other Female Rulers in Ancient Egypt
Hatshepsut (c. 1507 – 1458 BCE)
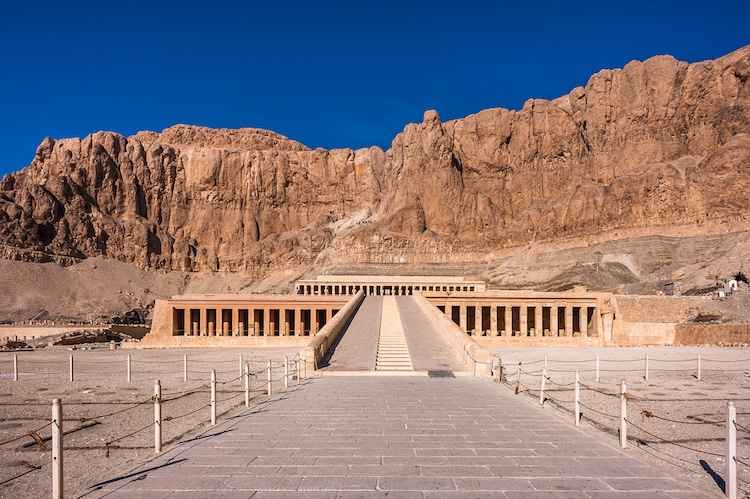

Temple of Hatshepsut, Luxor, Egypt (Photo: Siempreverde/DepositPhotos)
Hatshepsut (c. 1507 – 1458 BCE) was the second confirmed female pharaoh after Sobekneferu. She began as co-regent for her husband's son and heir, and after some time, adopted the full royal titularly. With a reign lasting 21 years, she had unprecedented power for a female ruler, maintaining peace in Egypt and constructing an extension to the Valley of the Kings so that her final resting place would be closer to her father, Thutmose I.
Nefertiti (c. 1370 – 1330 BCE)
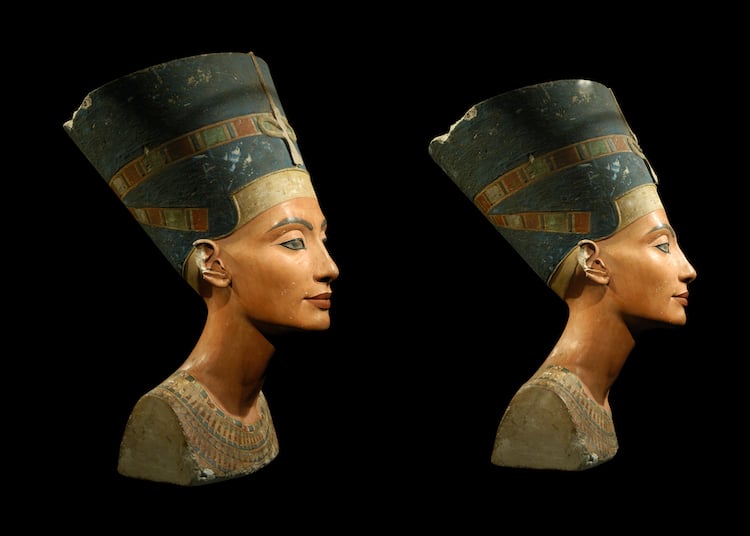

Bust of Nefertiti (Photo: wrangel/DepositPhotos)
Although not pharaoh herself, Nefertiti‘s (c. 1370 – 1330 BCE) name has persisted because she held a uniquely influential role as wife and queen, which we see in surviving depictions of her. Historians have gleaned that Nefertiti was a major proponent of Akhenaten's religious and cultural movement. She represented the female aspect of Aten while her husband represented the male—and both acted as a bridge between Aten and the Egyptian people.
Related Articles:
What is the Great Sphinx? Discover the History Behind the Ancient Egyptian Monument
Ancient Egyptians Wore Gold Sandals With Matching Toe Caps To Be Buried In
Ancient Egyptians Were Cat People: Exploring Felines and Gods in Art and Culture
Discover the History Behind the Obelisk, the Ancient Precursor to the Skyscraper